Read the manual thoroughly and understand all of the instructions, cautions, and warnings before using this equipment. If any section of the manual is not understood, contact your nearest authorized Generac IASD, or contact Generac Customer Service at 1-888-436-3722 (1-888-GENERAC), or www.generac.com with any questions or concerns.
Portable generator troubleshooting guide
Our troubleshooting guide provides step-by-step procedures to help resolve issues with portable generators, including start-up problems, running and shutdown issues, and rough running, stumbling, surging, or hunting. These procedures cover component-specific fuel, spark, air, and compression troubleshooting and offer helpful tips to avoid common issues.
Environment
This article applies to all gas-powered portable generators. While specific troubleshooting may vary depending on a generator's features, the basic principles and progressions remain consistent across most portable generators.
Troubleshooting table of contents
Introduction
Start-up troubleshooting
Portable generator battery troubleshooting
Quick reference table
Starting/running issues
Performance issues
Power generation issues
Breakers issues
Before starting troubleshooting, it is recommended to read the owner's manual as it contains essential information for unit startup, operation, maintenance schedule, and storage. Proper maintenance and storage can help prevent future troubleshooting.
See Where can I download a user manual for my Generac portable generator?
Efficient troubleshooting is all about taking things step by step in an operational progression.
First, make sure all the basic conditions of operation are met - such as having adequate fuel and oil, operating on level ground, or if using an electric start - a charged battery. It's crucial to double-check these basics, even if you think they're all good.
Next, we carefully follow the generator's start-up steps as missing or mixing up steps can lead to issues that might seem like bigger problems.
Finally, if those steps don't solve the issue, we take a closer look at the generator's specific start-up components to see if something's not working right. This ensures that any remaining issues are isolated to parts directly involved with the operation.
This organized approach helps us pinpoint the problem accurately but also underscores the importance of not overlooking simple solutions, making troubleshooting easier for everyone, whether you're an expert or not.
Refer to your owner's manual for model-specific startup requirements and procedures. See Where can I download a user manual for my Generac portable generator?
Before starting your portable generator, check that all pre-startup conditions are met. If you are experiencing issues with your unit, always double-check these conditions before troubleshooting.
- Verify oil level.
- Verify fuel level.
- Verify that the unit is secure on level ground, with proper clearance, and in a well-ventilated area.
- Nothing is plugged into the unit before starting.
- The battery is charged (if equipped).
Note: Portable generators with electronic fuel injection (EFI), require at minimum 10VDC battery charge to start, even if using the recoil.
Start-up troubleshooting: What to check first
1. Check startup procedure.
- Follow the owner's manual startup steps exactly
- Ensure all pre-startup conditions are met
2. Starting method.
Electric starts: Ensure the battery is adequately charged - generators require a minimum voltage to operate correctly.
-
- Check that all battery connections are clean and secure.
- See Electric Start Troubleshooting for more information
Recoil starts
-
- If an engine doesn't turn over easily, remove the spark plug and pull the recoil several times to relieve any built-up pressure, or allow the unit to sit for about 30 minutes.
- Ensure the spark plug boot cover is securely connected for proper spark delivery.
- See Manual Start (Recoil) Troubleshooting for more information
Note: Electronic Fuel Injection (EFI) models require 10VDC to operate, even when using the recoil.
3. How to approach starting issues based on last use.
- New: Focus on double-checking the starting procedure and pre-startup conditions are met.
- Previously started (less than 30 days): Check fuel and oil levels and look for minor, easily overlooked issues like loose connections.
- Not used recently (more than 30 days): Check the condition of the spark plug and air filter.
- The most common cause of startup issues with portable generators is old fuel left in the fuel system, clogging up the carburetor. Running the generator regularly or storing it properly can prevent these issues.
Starting and running issues
When a generator does not crank, the first step is to determine whether the starting mechanism is functioning correctly. Cranking is defined by the rotation of the engine's crankshaft, which is done by pulling the recoil or engaging the electric start.
Causes
- Broken, damaged starting mechanism (recoil or electric start)
- Dead or low battery
- Engine seizure
|
Issue
|
Possible cause
|
Actions
|
| Difficult to pull or does not pull at all | Obstructions, broken recoil, jammed flywheel, seized engine | Check for obstructions and inspect recoil and flywheel; if the engine is seized, contact Generac IASD |
| Pulls but does not return | Broken or loose recoil spring | Inspect the recoil spring or rewind if it's dislodged |
| Pulls smoothly, and the engine cranks, but it does not start | Unrelated to recoil itself | Check fuel, oil, spark plug, and air filter |
- If your generator is equipped with an electric start and the unit cannot turn over, there may be an issue with the battery, charging circuit, or cables.
- If the generator is equipped with a recoil start, attempt to start it using the recoil if possible. This will confirm that any starting issues are related to the electric starting mechanism.
|
Issue
|
Possible Cause
|
Action
|
| No noise or repetitive clicking noise when engaging the electric start | Dead or low battery | Check battery voltage and charge or replace the battery |
| Loose or corroded battery connections/terminals | Inspect battery terminals, clean off corrosion, inspect/tighten connections |
| Blown charging circuit fuse (if equipped) | Check the fuse and replace it if blown |
| Damaged wiring | Contact Generac IASD |
| Faulty starter | Contact Generac IASD |
Dead or low battery
For more information on portable battery charging guidelines, see Portable generator battery charging guidelines.
Starting and running issues can occur if the choke is improperly used, such as leaving it on too long or not using it during cold starts, disrupting the air-fuel mixture.
Vapor lock
Consider the possibility of a vapor lock, especially in hot conditions. Vapor lock occurs when fuel vaporizes before reaching the engine, disrupting fuel flow. If suspected, removing the spark plug and manually pulling on the recoil can release pressure. For units with vented gas caps, inspect the cap for vent blockages.
This indicates that the starting mechanism is turning the engine over (cranking) but not achieving ignition. This typically means the generator is not getting enough of, or the right combination of air, fuel, and spark.
Components and how they can contribute to starting issues
Fuel
- Fuel supply: Ensure the generator has adequate fuel supply. Running out of fuel is a common reason for cranking but not starting.
- Fuel shut-off valve: Check that the fuel shut-off valve is open. If closed, fuel cannot reach the engine, preventing startup.
- Fuel Quality: Assess the fuel quality for contaminants like water or stale fuel. Old or stale fuel is a common cause of carburetor issues.
- Oil level: Ensure the engine oil level is sufficient. Low oil levels may trigger a safety feature, such as a low oil pressure switch, preventing engine startup.
Air
- Choke position: Check the choke position to ensure it's not overused. Over-choking can flood the engine, inhibiting startup.
- Air filter:
Air/fuel Ratio
- Carburetor: Inspect the carburetor for potential issues such as flooding, stale fuel, or a stuck carburetor float. A stuck carburetor float can disrupt fuel flow and prevent startup.
- Intake Valve: Verify the intake valve for proper operation. A stuck intake valve, whether open or closed, can affect airflow and combustion, preventing engine startup.
Ignition
- Spark: Inspect the spark plug for signs of wear or fouling. A faulty spark plug can hinder ignition and cause starting issues.
Basic troubleshooting steps
1. Fuel supply and shut-off valve: Confirm the fuel level and ensure the shut-off valve is open.
2. Verify oil level: Inspect and verify the engine oil level.
3. Choke: Set choke to ON.
Attempt to start 3-4 times if you cannot start the unit, proceed to step 4.
4. Air filter: Remove and inspect - leave the air filter removed during the second start attempt.
5. Carburetor: Check the carburetor for issues like a stuck carburetor float. Lightly tapping the carburetor can dislodge the float. Alternatively, spraying carb cleaner directly into the carburetor can help with startup.
6. Spark plug, ignition, and oil sensor:
Checking the spark plug
- If the spark plug is wet, it may indicate fuel flooding the engine, suggesting potential issues with the carburetor or over-choking. In this case, focus on carburetor inspection, choke adjustment, and ensuring proper fuel flow.
- Overfilling the crankcase with oil, causing oil to push into the cylinder, could also cause a wet spark plug. Verify oil levels are correct and remove any excess oil.
- If the spark plug is dry, it suggests that fuel is not reaching the combustion chamber, indicating potential issues with the fuel supply or the fuel shutoff valve. In this scenario, prioritize fuel supply verification and shutoff valve inspection.
Note: Addressing old or stale fuel is crucial, as it's the number one cause of carburetor issues, especially when engines are stored with fuel and have not been started in over 30 days. Fuel additives like SEAFOAM can benefit wet and dry spark plug conditions. However, additives do not restore the quality of old or stale fuel.
Advanced Steps
For more complex issues requiring specialized knowledge or tools, we recommend contacting a Generac IASD.
A portable generator that starts but immediately shuts down is often caused by low oil levels, faulty sensors, or a clogged fuel line, preventing sustained operation.
Common causes
- Fuel system issue
- Clogged/blocked carburetor
- Clogged/blocked air filter
- Clogged/blocked fuel lines
- Fuel tank
Sensors
- Low oil level and oil pressure switch: This safety mechanism prevents engine damage by shutting down the generator if oil levels are insufficient to maintain proper lubrication.
Note: Ensure the generator is operated on level ground to prevent uneven oil distribution. Low oil levels could engage the oil pressure switch and trigger shutdown.
COsense Carbon Monoxide Sensor (if equipped): While generators should always be operated outside to prevent carbon monoxide buildup, it's important to note that factors such as blowing wind can sometimes trigger the carbon monoxide sensor. If you suspect the sensor is the cause of immediate shutdown, ensure the generator is being operated in a well-ventilated area and away from enclosed spaces.
Basic troubleshooting steps
- Verify the engine oil level.
- Verify fuel level.
- Check the fuel system for blockage or clogging.
- Check COsense™ (if equipped) for indicator lights.
- If a faulty low-oil pressure switch is suspected, contact a Generac IASD for diagnosis.
- If a faulty COsense™ indicator is suspected, contact a Generac IASD for diagnosis.
Preventing immediate shutdown
-
Regular maintenance: Check and maintain the oil level in your generator regularly according to the owner's manual. Avoid overfilling the oil reservoir.
-
Environmental Consideration: Always operate your generator in a well-ventilated outdoor area to prevent carbon monoxide buildup. If the generator is positioned with the exhaust downwind, it may blow exhaust into the CO sensor and trigger shutdown.
Common Causes
- Fuel supply: Running out of fuel is a common reason for sudden shutdowns during operation. Ensure the generator has an adequate fuel supply. Note that portable generator fuel tanks are typically gravity-fed, and having less than a quarter tank can lead to fuel delivery issues.
- Oil level and low oil pressure switch: Low oil levels can trigger an automatic shutdown to prevent engine damage. Check the oil level and refill it if necessary. If a faulty switch is suspected, seek professional diagnosis and replacement.
- COsense™ (If equipped): While generators should always be operated outside to prevent carbon monoxide buildup, it's important to note that factors such as blowing wind can sometimes trigger the carbon monoxide sensor. If you suspect the carbon monoxide sensor is the cause of the immediate shutdown, ensure the generator is well-ventilated and is being operated away from enclosed spaces.
If environmental factors are ruled out and your COsense™ is the cause of the immediate shutdown, seek a professional diagnosis. - Other faults, such as electrical issues or mechanical failures, can lead to sudden shutdowns during operation. If the sudden shutdown persists despite addressing fuel, oil, and safety features, other faults within the generator may be the cause. Contact a Generac IASD.
Starts, but runs rough
If your portable generator starts but runs rough and emits unnatural noises, it may be experiencing issues with the air-fuel mixture. Excessively rich and lean mixtures can lead to rough running and abnormal engine sounds.
-
Improper air-to-fuel mixture: An improper air-fuel mixture, whether excessively rich or lean, can disrupt engine performance and cause rough running.
-
Airflow, fuel supply, and combustion: Airflow, fuel supply, and combustion are critical actions where air and fuel interact to power the generator. Disruptions in these processes can lead to rough running and unusual noises.
-
Airflow: Components such as the air filter, choke, and intake valve regulate engine airflow. Any blockage or malfunction in these parts can disrupt the air-fuel ratio.
-
Fuel flow: Ensure the fuel supply and inline fuel filters are clean and adequate. Blockages or impurities from old fuel in the fuel line or tank can disrupt fuel flow.
-
Combustion: Proper combustion requires the right balance of air and fuel. Issues such as fouled spark plugs, dirty carburetors, or malfunctioning valves can lead to incomplete combustion.
Basic troubleshooting steps
1. Fuel supply: Check the fuel supply and inline fuel filters for cleanliness and adequacy. Ensure no blockages and remove old/stale fuel to prevent impurities in the fuel line or tank.
2. Choke position: Verify that the choke is not overused. Over-choking can disrupt airflow.
3. Spark plug: Inspect the spark plug for wear, fouling, or misfiring. A malfunctioning spark plug can disrupt combustion.
4. Air filter: Check the air filter for dirt or blockages. A dirty air filter can restrict airflow, causing rough running and abnormal engine sounds
Advanced
For more complex issues or those requiring specialized knowledge or tools, contact a Generac IASD for diagnosis.
1. Carburetor: Examine the carburetor for dirt, clogs, or maladjustments. Issues with the carburetor can affect the fuel-air mixture and are the most common cause of minor engine problems.
2. Intake valve: Ensure the intake valve is in proper clearance and functioning correctly. Malfunction valves can disrupt airflow and combustion efficiency.
3. Engine Compression: Loss of engine compression can result in poor combustion.
Stumbling, surging, or hunting is typically caused by an inconsistent fuel supply, clogged air filter, or improper fuel-to-air ratio, leading to fluctuations in engine speed.
Identifying stumbling, surging, or hunting in portable generator
Stumbling typically occurs when a generator attempts to start but fails to run smoothly, often due to improper choke setting or air-fuel mixture problems. Surging refers to a generator running erratically, increasing and decreasing in speed, which can be caused by issues like dirty carburetor or improper fuel mixture. Hunting is different, it is characterized by a more rhythmic oscillation between high and low RPMs.
Key signs
- Stumbling: The generator starts but runs unevenly or stops shortly after starting.
- Surging: The generator's engine speed fluctuates widely without any change in load.
- Hunting: Regular oscillation in engine speed (as opposed to more erratic surging).
Troubleshooting
Basic
1. Check the choke: Ensure the choke is not left ON (closed) after starting. The choke is typically only used when starting a cold engine and is turned OFF (open) when the engine warms up.
2. Fuel supply: Ensure fuel is fresh and at adequate levels. Old/stale fuel is the number one cause of dirty carburetors and numerous other issues. Check that the fuel supply and inline fuel filter are free of debris.
3. Air filter: Ensure the air filter is clean. A dirty air filter will prevent air flow and affect the fuel mixture.
Advanced steps
1. Carburetor cleaning: After basic troubleshooting, inspecting and cleaning the carburetor is the next step.
2. Carburetor adjustments: Adjustments to the carburetor for air and fuel mixture require expertise; contact a Generac IASD for diagnosis and adjustment.
3. Electrical checks: If electrical issues are suspected, contact a Generac IASD for diagnosis.
4. Governor adjustment and hunting: If basic troubleshooting is ineffective at resolving a hunting generator, adjustments to the governor may be necessary. If a governor issue is suspected, we recommend contacting a Generac IASD for diagnosis.
Note: Engine speed increases and decreases - This is normal as generator startup and loads vary.
A portable generator that starts but lacks power indicates an issue with electrical production. Common problems include generator overload, dirty air filters, clogged spark arrestors, and the need for potential engine servicing. Unlike hunting, stumbling, or surging - which involve inconsistent engine performance - this problem involves smooth engine operation but insufficient power generation.
Key signs
- Reduced output: The generator runs, but appliances or tools operate slower than usual or lack sufficient power.
- Poor engine performance: The engine sounds strained, runs unevenly, or shuts down under load.
- Visual exhaust smoke: Excessive smoke can indicate incomplete combustion, often related to air intake/exhaust systems issues or a fouled spark plug.
Troubleshooting
Basic
1. Check for overload: Verify that the total electrical load is within the generator's capacity. Reduce the load if necessary and reset any tripped circuit breakers.
Note: The difference between appliance starting (surge) wattage and running wattage is commonly overlooked. See What Does Surge/Starting Wattage Mean? for more information.
2. Air filter: Inspect the air filter. A dirty air filter restricts airflow and will reduce engine performance.
3. Spark arrestor: A clogged spark arrestor can restrict exhaust flow and reduce engine performance.
Advanced
1. Fuel system check: Inspect the fuel lines, filter, and pump. Old/stale fuel can cause poor engine performance and is the number one cause of generator issues.
2. Engine service: The engine may require servicing if basic troubleshooting does not resolve the issue. This could involve checking and adjusting the valve clearance.
3. Exhaust system examination: Blockages or leaks in the exhaust system can lead to performance issues. If exhaust system examination is suspected, it is recommended to consult a Generac IASD.
Bogging down under load occurs when a generator starts and appears to run smoothly until a load is applied; at this point, it struggles to maintain power. While the signs are similar to lack of power, such as uneven running and straining, they are distinguished by the moment these signs occur. Bogging down relates explicitly to the generator's response to an applied load rather than a consistent underperformance.
Key signs
- Immediate strain under load: The generator runs fine until a load is applied, then quickly loses power or shuts down.
- Abnormal engine noises: Upon applying load, the engine may make unusual noises, indicating it is struggling to meet the demands of the load.
Troubleshooting
Basic steps
1. Check for overload: Verify that the total electrical load is within the generator's capacity. Reduce the load if necessary and reset any tripped circuit breakers.
Note: The difference between appliance starting (surge) wattage and running wattage is commonly overlooked. See What Does Surge/Starting Wattage Mean? for more information.
2. Spark arrestor: A clogged spark arrestor can impair engine performance. Check and clean the spark arrestor to ensure it does not contribute to the issue.
3. Inspect connected loads for short circuits: Disconnect and reconnect all loads individually. This can help identify if a particular load is causing an overload or has a short circuit.
Advanced
1. Fuel system check: Inspect the fuel lines and filter, ensuring adequate fuel flow to the engine. Old/stale fuel is the number one cause of generator issues. Eliminating fuel issues as a contributing factor aids in appropriately narrowing down the culprit.
2. Carburetor cleaning: A dirty or clogged carburetor can cause the engine to underperform under load.
3. Electrical Diagnosis: If the generator's electrical system is suspected, it is recommended that you consult a Generac IASD for diagnosis.
4. Comprehensive engine inspection: If basic troubleshooting cannot resolve the issue and the generator continues to bog down under load, contact a Generac IASD for a more thorough engine inspection.
This section addresses issues with a portable generator that starts and runs fine but fails to produce electrical output. It covers simple issues to more complex problems like alternator demagnetization and outlines initial conditions for effective diagnosis.
Identifying lack of electrical output in portable generators
Before starting troubleshooting, ensure the generator is running without any connected loads.
Key signs
- No power in any outlet: Check multiple outlets to confirm a total lack of output.
- One outlet works, others do not: This could indicate a localized issue such as a tripped breaker specific to the non-working outlets or wiring faults.
- Functional engine: Indicates the issue is likely electrical rather than mechanical.
Note:
- Resetting breakers: Remember to reset any necessary breakers while running the generator.
- Starting conditions: Always start the generator with no loads connected.
Basic troubleshooting
1. Inspect Main Line Circuit Breaker (MLCB)
- Check if the MLCB is open. The proper operating position is "closed," allowing power to flow through the system. Power is disconnected if the breaker is in the "open" position.
2. Inspect GFCI outlets (if equipped)
- Reset any tripped GFCI receptacles. These can often trip due to minor faults or exposure to moisture.
3. Connection and cords
- If possible, test the connection and cord on a known power source to rule out cord issues. Ensure all connections are secure and replace any defective or damaged cords.
Tripping breakers in portable generators can indicate several potential issues. Proper troubleshooting requires understanding different breaker types and how to systematically address the causes of trips.
Breaker types and characteristics
120VAC Receptables breakers
- Typically, push-button breakers are for individual or small groups of outlets.
- Common causes of tripping include overloads or short circuits in connected devices or cord sets
240VAC Main Breakers
- Usually, toggle or pull breakers control the total output of the generator.
- Trip due to overall generator overload or significant imbalances between connected loads.
Ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) breakers
- Designed to trip upon detecting ground faults.
- GFCI tripping due to clean power requirements
- GFCI breakers can trip if the connected load is sensitive to power quality.
- Not all appliances will work with GFCI outlets, see Why won't my fridge run off my portable generator?
Circuit breakers
All electrical outlets are required to have circuit breaker protection. Breakers are designed to protect the generator against overload. They will handle a momentary surge that exceeds the breaker rating, but if the high current continues, the breaker trips, and all the outlets stop working.

GFCI receptacles
The GFCI receptacle senses electrical “leaks”—electrical current is escaping the device and taking a different path to ground than the one provided. Leaks are usually caused by water, dust, worn insulation, a defective electrical appliance, or human skin. A GFCI will trip and shut off power when a leak is detected to protect against electric shock, electrocution, burns, and fires.
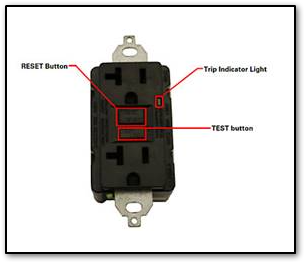
What causes tripping?
All electrical outlets are required to have circuit breaker protection. Breakers are designed to protect the generator against overload. They will handle a momentary surge that exceeds the breaker rating, but if the high current continues, the breaker trips and all the outlets stop working.
Understanding wattage requirements: Starting/Surge vs. Running Wattage
Note: Ensure the generator's total and per-circuit output meets connected devices' starting and running wattage requirements to prevent tripping from overload.
Initial Conditions for Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
1. Identifying and resetting the problematic breaker
- Use the push-button for the 120VAC breakers or the pull switch 240VAC breakers to reset
- A breaker that trips immediately upon reset without load may be faulty
2. Isolating the issue
- Gradually reconnect devices one at a time to pinpoint which load causes the breaker to trip
- Test different outlets to determine if the issue is localized.
3. Check and test cord sets
- Replace and test different cord sets to eliminate the possibility of defective or damaged cords as the cause of tripping.
Single incident vs. routine tripping: If a breaker trips once, it could be due to a temporary overload. Frequent tripping, however, suggests a more severe issue, such as persistent overload, a need for breaker replacement, or an internal fault within the generator.
Additional considerations
-
Using multiple connections and extension cords dramatically increases the chances of tripping the GFCI.
-
Multi-outlet strips should never be "daisy chained" or connected in series, as this creates a safety hazard and increases the risk of electrical overload.
-
Ensure all your cord connections are dry (not in the rain or standing water)—this is unsafe and is likely to cause electrical leakage (and GFCI trips).
-
Older household appliances (freezers, refrigerators, etc.) may be prone to electrical leakage, which can cause the GFCI to trip. If this happens, contact the appliance manufacturer for more information.
-
Never operate a portable generator in the rain. Doing so can damage the generator and cause a potential electrical hazard.
When to contact a Generac IASD
If routine tripping persists after basic troubleshooting, professional help is recommended, especially when dealing with complex electrical faults that could involve internal wiring or breaker integrity.



